Table of contents
- Introduction to FMEA in Automotive Testing
- Learning Objectives of Failure Modes Effect Analysis (FMEA)
- Benefits of Failure Modes Effect Analysis (FMEA)
- Application Examples of Failure Modes Effect Analysis (FMEA)
- What Is A Failure Mode?
- Why to use Failure Modes Effect Analysis (FMEA)?
- When to Conduct an FMEA?
- History of Failure Modes Effect Analysis (FMEA)
- Advantages & Disadvantages of FMEA in Automotive Industry
Introduction to FMEA in Automotive Testing
Failure Modes Effect Analysis (FMEA) is a proactive risk management tool used in the automotive industry to identify and prioritize potential failure modes in a product or system. It helps to assess the likelihood, severity and detectability of each failure mode and to develop action plans to eliminate or mitigate the risk of the failure occurring. FMEA is commonly used in the automotive industry during the design, development, and testing phases to ensure that the product is reliable and safe for use. The process of FMEA involves identifying all the potential failure modes, evaluating their impact, determining the cause and effects of each failure mode, and developing corrective actions to eliminate or reduce the risk of failure.
Learning Objectives of Failure Modes Effect Analysis (FMEA)
- To understand the use of Failure Modes Effect Analysis (FMEA)
- To learn the steps to developing FMEAs
- To summarize the different types of FMEAs
- To learn how to link the FMEA to other Process tools
Benefits of Failure Modes Effect Analysis (FMEA)
- Allows us to identify areas of our process that most impact our customers
- Helps us identify how our process is most likely to fail
- Points to process failures that are most difficult to detect
Application Examples of Failure Modes Effect Analysis (FMEA)
Manufacturing: A manager is responsible for moving a manufacturing operation to a new facility. He/she wants to be sure the move goes as smoothly as possible and that there are no surprises.
Design: A design engineer wants to think of all the possible ways a product being designed could fail so that robustness can be built into the product.
Software: A software engineer wants to think of possible problems a software product could fail when scaled up to large databases. This is a core issue for the Internet.
What Is A Failure Mode?
The FMEA tool is a part of the overall APQP process. It is used through the design and production process of it to identify where failures can occur, how frequently it could happen and whether or not we can detect those failures.
The FMEA is a step-by-step process that looks at the vehicle design, the production processes, and tests, and finally how the vehicle will be used by the end customer and looks for all areas where failures could occur.
The FMEA uses a spreadsheet format and uses inputs from all the team members to complete the form. FMEA can be done on a design (DFMEA), production process (PFMEA) and even quality FMEAs can be done. There is no end of use for this powerful tool.
A Failure Mode is:
- The way in which the component, subassembly, product, input, or process could fail to perform its intended function
- Failure modes may be the result of upstream operations or may cause downstream operations to fail
- Things that could go wrong
Why to use Failure Modes Effect Analysis (FMEA)?
- A methodology that facilitates process improvement
- Identifies and eliminates concerns early in the development of a processor design
- Improve internal and external customer satisfaction
- Focuses on prevention
- FMEA may be a customer requirement (likely contractual)
- FMEA may be required by an applicable Quality Management System Standard (possibly ISO)
A structured approach to:
- Identifying the ways in which a product or process can fail
- Estimating risk associated with specific causes
- Prioritizing the actions that should be taken to reduce risk
- Evaluating design validation plan (design FMEA) or current control plan (process FMEA)
When to Conduct an FMEA?
- Early in the process improvement investigation
- When new systems, products, and processes are being designed
- When existing designs or processes are being changed
- When carry-over designs are used in new applications
- After system, product, or process functions are defined, but before specific hardware is selected or released to manufacturing
History of Failure Modes Effect Analysis (FMEA)
- First used in the 1960s in the Aerospace industry during the Apollo missions.
- In 1974, the Navy developed MIL-STD 1629 regarding the use of FMEA.
- In the late 1970s, the automotive industry was driven by liability costs to use FMEA.
- Later, the automotive industry saw the advantages of using this tool to reduce risks related to poor quality.
How does FMEA works in Automotive Industry?
FMEA works in the automotive industry by breaking down the system into its components and identifying the potential failure modes for each component.
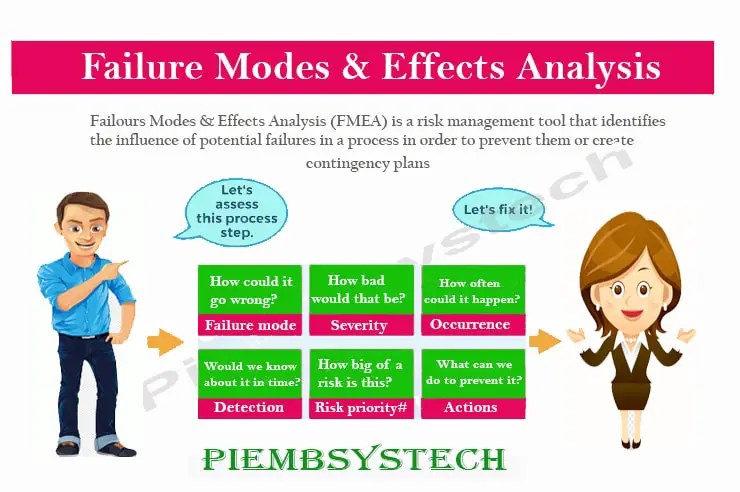
The process of FMEA involves several steps:
- Identify the components: This step involves breaking down the system into its individual components and identifying their functions.
- Identify the potential failure modes: For each component, the potential failure modes are identified and documented.
- Evaluate the severity of the failure mode: The impact or severity of the failure mode on the system is rated based on a standardized scale.
- Evaluate the likelihood of occurrence: The likelihood of the failure mode occurring is evaluated based on a standardized scale.
- Evaluate the detectability of the failure mode: The ease of detecting the failure mode is evaluated based on a standardized scale.
- Determine the Risk Priority Number (RPN): The RPN is calculated by multiplying the severity, likelihood, and detectability scores of each failure mode.
- Develop corrective actions: Based on the RPN, the highest priority failure modes are addressed first, and corrective actions are developed to eliminate or mitigate the risk of the failure mode occurring.
- Implement and verify corrective actions: The corrective actions are implemented and the effectiveness of the actions is verified to ensure that the risk has been reduced.
FMEA is a continuous process, and the analysis should be updated regularly to reflect changes in the system and to address new potential failure modes.
Measurement of Failure Modes Effect Analysis (FMEA) in the Automotive
The measurement of the Failure Modes Effect Analysis (FMEA) in the automotive industry involves determining the Risk Priority Number (RPN) for each potential failure mode. The RPN is calculated as follows:
RPN = Severity (S) x Occurrence (O) x Detection (D)
Where:
- Severity (S) is a numeric rating of the potential impact of the failure mode on the system, customer, or end-user. This is rated on a scale from 1 to 10, with 10 being the highest level of severity.
- Occurrence (O) is a numeric rating of the likelihood of the failure mode occurring. This is rated on a scale from 1 to 10, with 10 being the highest likelihood of occurrence.
- Detection (D) is a numeric rating of the ability to detect the failure mode before it affects the system or end-user. This is rated on a scale from 1 to 10, with 10 being the highest ability to detect the failure mode.
The RPN is used to prioritize the failure modes and determine which failure modes require immediate attention. The higher the RPN, the higher the priority for addressing the failure mode. The FMEA team can then develop corrective actions to eliminate or mitigate the risk of the failure mode occurring. The RPN is recalculated after the corrective actions have been implemented to ensure that the risk has been effectively reduced.
Advantages & Disadvantages of FMEA in Automotive Industry
As we understood that the FMEA is a vital part of automotive industry to follow the safety standard, it is also having both advantages and disadvantages. Lets discuss about it with some fruitfull technical points.
Advantages of Failure Modes Effect Analysis (FMEA) in Automotive
- Improved Safety: FMEA helps to identify and mitigate potential safety hazards in the design and development of automotive products, leading to safer products for consumers.
- Improved Reliability: FMEA helps to identify and address potential failure modes in a systematic manner, resulting in more reliable products.
- Increased Customer Satisfaction: FMEA helps to ensure that automotive products meet customer needs and expectations, leading to increased customer satisfaction.
- Early identification of potential problems: FMEA enables the identification of potential problems at an early stage in the development process, allowing for proactive corrective action to be taken.
- Improved Design: FMEA helps to identify areas for improvement in the design of automotive products, leading to more efficient and effective products.
Disadvantages of Failure Modes Effect Analysis (FMEA) in Automotive
- Time-consuming: FMEA can be a time-consuming process, especially for complex systems, requiring a significant investment of time and resources.
- Limited information: FMEA is only as effective as the information available, and the absence of accurate and complete data can limit the effectiveness of the analysis.
- Cost: Implementing FMEA can be expensive, especially for small companies or organizations with limited resources.
- Limited predictability: FMEA is a subjective process, and the likelihood and severity ratings can be difficult to determine, leading to limited predictability in the results.
- Limited impact: FMEA is only effective if the corrective actions identified are implemented, and the impact of the analysis can be limited if the recommended actions are not taken.
Discover more from PiEmbSysTech - Embedded Systems & VLSI Lab
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.




