Flow Control in RS232
Flow control in RS232 communication refers to the mechanism that manages the data transmission between devices to prevent data loss, buffer overflow, and ensure smooth communication. Flow control is essential when data is being transmitted at different speeds or when the receiving device cannot handle the incoming data as quickly as it is being sent.
There are two main types of flow control used in RS232 communication:
1. Hardware Flow Control (RTS/CTS)
- RTS (Request to Send) and CTS (Clear to Send) are signals used for hardware-based flow control in RS232 communication.
- RTS is a signal sent by the transmitting device to indicate it is ready to send data, and the receiving device responds with CTS to signal that it is ready to receive data.
- If the receiving device is not ready to accept data, it can negate the CTS signal, effectively telling the transmitter to pause data transmission. When the receiver is ready, it will assert CTS, allowing data transmission to resume.
- This type of flow control is hardware-driven and requires additional physical lines (RTS and CTS) between the devices.
2. Software Flow Control (XON/XOFF)
- Software flow control involves sending special control characters within the data stream to manage the flow of data.
- XON (Transmitter On) and XOFF (Transmitter Off) are the control characters used in this system.
- XON is sent by the receiving device to the transmitting device to indicate that it is ready to receive data. When the receiving buffer is full or it needs to temporarily stop receiving data, the receiver sends XOFF to instruct the transmitter to pause transmission.
- This type of flow control does not require extra physical lines, as the flow control is implemented through software by sending special characters in the data stream.
Key Differences Between Hardware and Software Flow Control
- Hardware Flow Control: Requires additional control lines (RTS/CTS) for communication, typically used when high-speed communication or reliable data transfer is critical.
- Software Flow Control: Uses data characters (XON/XOFF) for flow control, suitable for slower or less critical communication but more flexible as it does not need extra lines.
Why Flow Control is Important?
- Prevents Data Loss: Flow control prevents the transmitter from sending data faster than the receiver can handle, reducing the chance of data overflow or loss.
- Ensures Reliable Communication: In cases of high-speed or continuous data streams, flow control ensures both devices remain synchronized and operate at optimal speeds.
- Optimizes Buffer Usage: Proper flow control ensures the receiver’s buffer does not overflow, allowing for smooth and uninterrupted data transmission.
Common RS232 Connectors
RS232 communication uses various connectors to establish serial connections between devices. The type of connector used depends on the number of signal lines needed and the specific application. Below are some of the most common RS232 connectors:
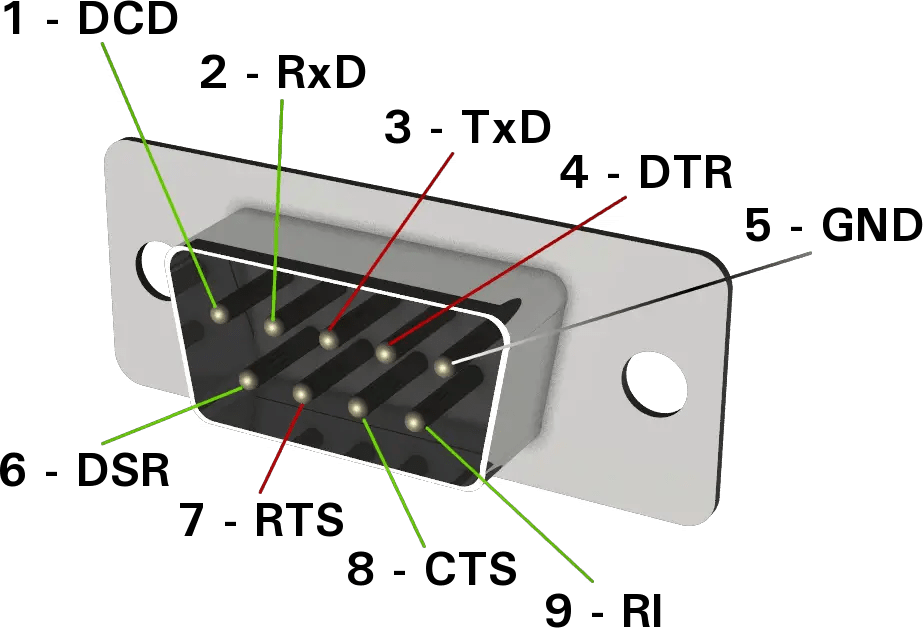
1. DB9 Connector
- The DB9 connector is one of the most commonly used RS232 connectors. It has 9 pins and is typically found in many computer and peripheral devices, such as serial ports on PCs and modems.
- Pinout:
- Pin 1: DCD (Data Carrier Detect)
- Pin 2: RXD (Receive Data)
- Pin 3: TXD (Transmit Data)
- Pin 4: DTR (Data Terminal Ready)
- Pin 5: GND (Ground)
- Pin 6: DSR (Data Set Ready)
- Pin 7: RTS (Request to Send)
- Pin 8: CTS (Clear to Send)
- Pin 9: RI (Ring Indicator)
- The DB9 is often used for devices requiring simple serial communication like printers, scanners, or older peripherals.
2. DB25 Connector
- The DB25 connector is a larger connector with 25 pins and is commonly used in older serial devices. It was historically used for communication in RS232 serial ports on early PCs, modems, and printers.
- Pinout:
- Similar to the DB9, but with more pins to support additional control lines and signals for more complex serial communication setups.
- DB25 was commonly used for RS232 communication with multiple devices that required more than just the basic TX, RX, and Ground lines.
3. RJ45 Connector
- Although primarily used for Ethernet connections, the RJ45 connector can also be used for RS232 communication in some specialized setups, especially when RS232 to Ethernet converters are used.
- Pinout:
- The pinout of RJ45 connectors for RS232 communication depends on the specific device and conversion method. In some cases, the RJ45 might carry a single signal or multiple signals.
- RJ45 connectors are often used for space-saving applications, like in networking devices or serial-over-IP systems.
4. DE9 Connector
- The DE9 is similar to the DB9 connector and is used for RS232 serial communication. It has a 9-pin configuration but is slightly more compact than the DB9. This connector is sometimes seen in compact devices or embedded systems.
- Pinout:
- Similar to the DB9 connector but with a more compact form factor.
5. Male and Female RS232 Connectors
- RS232 connectors are typically available in male and female versions. The male connector has pins (protruding), while the female connector has sockets (receptacles).
- The choice of male or female depends on the device, with male connectors generally found on transmitting devices and female connectors on receiving devices.
6. Sub-D Connectors
- The Sub-D connector is a standard connector for RS232 communication. The DB9 and DB25 are examples of Sub-D connectors, which feature a D-shaped metal shell with multiple pins inside.
- Sub-D connectors are robust and widely used in industrial applications, machine controls, and peripheral devices that need a secure, durable connection.
Types of RS232 Ports
RS232 ports are used for serial communication between devices, and while the communication standard itself remains the same, the types of RS232 ports vary in terms of their physical configurations, signal lines, and intended applications. The most common types of RS232 ports include:
1. DB9 RS232 Port
- Description: The DB9 port is one of the most commonly used RS232 ports. It features a 9-pin D-sub connector and is typically used in computers, modems, and peripherals like printers and scanners.
- Common Applications: This port is often used for simple serial connections where only basic data transmission and control signals are needed. It is also common on older PCs and communication devices.
2. DB25 RS232 Port
- Description: The DB25 port is a 25-pin connector used for RS232 communication. It was commonly used on older PCs and modems and can support more control signals than the DB9 port.
- Common Applications: The DB25 port was typically found on older serial communication devices and was used for applications requiring multiple control lines, such as industrial equipment or more complex data transfer systems. It is less common today due to the smaller and more compact DB9 connector.
3. RJ45 RS232 Port
- Description: The RJ45 port is typically used for Ethernet communication, but it can also serve as an RS232 connection in specialized configurations, especially in RS232-to-Ethernet adapters or networked serial devices.
- Common Applications: RJ45 RS232 ports are primarily used in networking applications where serial data is transmitted over an Ethernet connection. It’s common in serial-over-IP systems and other industrial networking solutions that combine serial and Ethernet communication.
4. Sub-D RS232 Port
- Description: The Sub-D connector refers to a family of connectors with a D-shaped metal shell. The DB9 and DB25 connectors are both examples of Sub-D connectors used for RS232 communication.
- Common Applications: Sub-D RS232 ports are commonly found in industrial settings, embedded systems, and machine control devices, offering a secure and durable connection for long-term usage.
5. Mini-DB9 RS232 Port
- Description: The Mini-DB9 is a smaller version of the DB9 port, typically found in compact devices and embedded systems. It still has 9 pins but in a more compact form factor.
- Common Applications: It is used in small form-factor devices, embedded electronics, and portable equipment that require serial communication without taking up too much space.
6. PC COM Port
- Description: A PC COM port (or serial port) is a standard port found on many desktop PCs and laptops. It may use either a DB9 or DB25 connector for RS232 communication.
- Common Applications: These COM ports were commonly used for connecting peripherals like modems, mice, and printers to the PC in the past. While rare in modern PCs, they are still used in legacy systems or specialized equipment.
7. RS232 Over USB Port
- Description: Modern devices may use an RS232 to USB converter to provide RS232 communication through a USB port. These adapters allow older RS232 devices to be connected to modern computers that lack traditional RS232 ports.
- Common Applications: Common in modern PCs and laptops to connect to legacy serial devices like printers, industrial controllers, or modems that only support RS232 but need to be used with USB-only computers.

You must be logged in to post a comment.